Information
- Publication Type: Conference Paper
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: May 2007
- ISBN: 978-1-56881-337-0
- Publisher: Canadian Human-Computer Communications Society
- Location: Montreal, Canada
- Lecturer: Markus Giegl
- Editor: Christopher G. Healey and Edward Lank
- Booktitle: Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2007
- Conference date: 28. May 2007 – 30. May 2007
- Pages: 159 – 168
- Keywords: real-time shadowing, shadows, shadow maps, large environemnts
Abstract
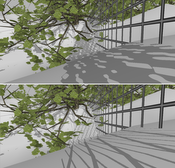
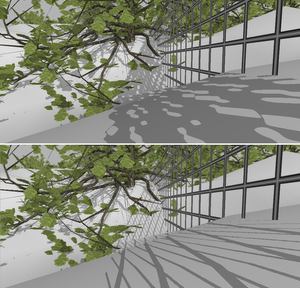
Too little shadow map resolution and resulting undersampling artifacts, perspective and projection aliasing, have long been a fundamental problem of shadowing scenes with shadow mapping.We present a new smart, real-time shadow mapping algorithm that virtually increases the resolution of the shadow map beyond the GPU hardware limit where needed. We first sample the scene from the eye-point on the GPU to get the needed shadow map resolution in different parts of the scene. We then process the resulting data on the CPU and finally arrive at a hierarchical grid structure, which we traverse in kd-tree fashion, shadowing the scene with shadow map tiles where needed.
Shadow quality can be traded for speed through an intuitive parameter, with a homogeneous quality reduction in the whole scene, down to normal shadow mapping. This allows the algorithm to be used on a wide range of hardware.
Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@inproceedings{GIEGL-2007-FVS,
title = "Fitted Virtual Shadow Maps",
author = "Markus Giegl and Michael Wimmer",
year = "2007",
abstract = "Too little shadow map resolution and resulting undersampling
artifacts, perspective and projection aliasing, have long
been a fundamental problem of shadowing scenes with shadow
mapping. We present a new smart, real-time shadow mapping
algorithm that virtually increases the resolution of the
shadow map beyond the GPU hardware limit where needed. We
first sample the scene from the eye-point on the GPU to get
the needed shadow map resolution in different parts of the
scene. We then process the resulting data on the CPU and
finally arrive at a hierarchical grid structure, which we
traverse in kd-tree fashion, shadowing the scene with shadow
map tiles where needed. Shadow quality can be traded for
speed through an intuitive parameter, with a homogeneous
quality reduction in the whole scene, down to normal shadow
mapping. This allows the algorithm to be used on a wide
range of hardware.",
month = may,
isbn = "978-1-56881-337-0",
publisher = "Canadian Human-Computer Communications Society",
location = "Montreal, Canada",
editor = "Christopher G. Healey and Edward Lank",
booktitle = "Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2007",
pages = "159--168",
keywords = "real-time shadowing, shadows, shadow maps, large
environemnts",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2007/GIEGL-2007-FVS/",
}

 Preprint
Preprint