Show images of current Projects | Years: 2018 - 2019 - 2020.
VRVis Competence Center
The VRVis K1 Research Center is the leading application oriented research center in the area of virtual reality (VR) and visualization (Vis) in Austria and is internationally recognized. You can find extensive Information about the VRVis-Center here
X-Mas Cards
Every year a christmas card showing aspects of our research projects is produced and sent out.Advanced Visual and Geometric Computing for 3D Capture, Display, and Fabrication
This Marie-Curie project creates a leading European-wide doctoral college for research in Advanced Visual and GeometricComputing for 3D Capture, Display, and Fabrication.
Smart Communities and Technologies: 3D Spatialization
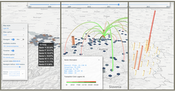
The Research Cluster "Smart Communities and Technologies" (Smart CT) at TU Wien will provide the scientific underpinnings for next-generation complex smart city and communities infrastructures. Cities are ever-evolving, complex cyber physical systems of systems covering a magnitude of different areas. The initial concept of smart cities and communities started with cities utilizing communication technologies to deliver services to their citizens and evolved to using information technology to be smarter and more efficient about the utilization of their resources. In recent years however, information technology has changed significantly, and with it the resources and areas addressable by a smart city have broadened considerably. They now cover areas like smart buildings, smart products and production, smart traffic systems and roads, autonomous driving, smart grids for managing energy hubs and electric car utilization or urban environmental systems research.
3D spatialization creates the link between the internet of cities infrastructure and the actual 3D world in which a city is embedded in order to perform advanced computation and visualization tasks. Sensors, actuators and users are embedded in a complex 3D environment that is constantly changing. Acquiring, modeling and visualizing this dynamic 3D environment are the challenges we need to face using methods from Visual Computing and Computer Graphics. 3D Spatialization aims to make a city aware of its 3D environment, allowing it to perform spatial reasoning to solve problems like visibility, accessibility, lighting, and energy efficiency.
Visual Computing: Illustrative Visualization
The central focus of our research is to understand visual abstraction. Understanding means 1. to identify meaningful visual abstractions, 2. to assess their effectiveness for human perception and cognition and 3. to formalize them to be executable on a computational machinery. The outcome of the investigation is useful for designing visualizations for a given scenario or need, whose effectiveness can be quantified and thus the most understandable visualization design can be effortlessly determined. The science of visualization has already gained some understanding of structural visual abstraction. When for example illustrators, artists, and visualization designers convey certain structure, or visually express how things look, we can often provide a scientifically-founded argument whether and why is their expression effective for human cognitive processing. What has not been given sufficient scientific attention to, is advancing the understanding of procedural visual abstraction, in other words investigating visual means that convey what things do or how things work. This missing piece of knowledge would be very useful for visual depiction of processes and dynamics that are omnipresent in science, technology, but also in our everyday lives. The upcoming project will therefore investigate theoretical foundations for visualization of processes. Physiological processes that describe the complex machinery of biological life will be picked as a target scenario. The reason for this choice is two-fold. Firstly, these processes are immensely complex, are carried-out on various spatial and temporal levels simultaneously, and can be sufficiently understood only if all scales are considered. Secondly, physiological processes have been modeled as a result of intensive research in biology, systems biology, and biochemistry and are available in a form of digital data. The goal will be to visually communicate how physiological processes participate on life by considering the limitations of human perceptual and cognitive capabilities. By solving individual visualization problems of this challenging target scenario, the research will provide first pieces of understanding of procedural visual abstractions that are generally applicable, beyond the chosen target domain. Prototype implementation of the developed technology is available at the GitHub repository: https://github.com/illvisation/
Prototype implementation of the developed technology is available at the GitHub repository:
https://github.com/illvisation/
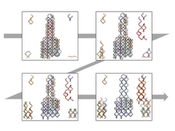
cellVIEW
cellVIEW is a new tool that provides fast rendering of very large biological macromolecular scenes and is inspired by state-of-the-art computer graphics techniques. Click here for additional information.
Invited Talks
18.11.2016: Arthur J. Olson, Envisioning the Visible Molecular Cell
17.10.2016: Kwan-Liu Ma, Emerging Topics for Visualization Research: Part1, Part2
07.10.2016: Marc Streit, From Visual Exploration to Storytelling and Back Again
04.12.2015: Jan Palacek, Visual Analysis of Protein Complexes: From Protein Interaction to Cellular Processes
19.04.2013: Jan Koenderink, Shape in Visual Awareness
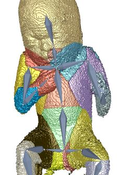
Real-Time Shape Acquisition with Sensor-Specific Precision
Acquiring shapes of physical objects in real time and with guaranteed precision to the noise model of the sensor devices.Path-Space Manifolds for Noise-Free Light Transport
The project aims to develop new statistical and algorithmic methods to improve light-transport simulation for offline rendering.A Test Suite for Photorealistic Rendering and Filtering
This project will research methods to test and compare global-illumination algorithms as well as filtering algorithms, and also develop test data sets for this purpose.MAKE-IT-FAB: Modeling of Shapes for Personal Fabrication
The aim of this project is to investigate and to contribute to shape modeling and geometry processing for personal fabrication---a trend that currently receives intensified attention in the science and industry. Our goal is to contribute novel algorithmic solutions for fabrication-aware shape processing and interactive modeling.ILLUSTRARE: Integrative Visual Abstraction of Molecular Data
FWF - I 2953-N31Integrative Visual Abstraction of Molecular Data
BioNetIllustration: User Centric Illustrations of Biological Networks
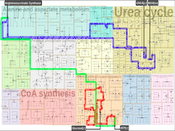
In living systems, one molecule is commonly involved in several distinct physiological functions. The roles of molecules are commonly summarized in pathway diagrams, which, however, are abstract, hierarchically nested and thus is difficult to comprehend especially by non-expert audience. The primary goal of this research in visualization is to intuitively support the comprehensive understanding of relationships among biological networks using interactively computed illustrations. Illustrations, especially in textbooks of biology are carefully designed to clearly present reactions between organs as well as interactions within cells. Automatic generation of illustrative visualizations of biological networks is thus the technical content of this proposal. Automatic generation of hand-drawn illustrations has been a challenging task due to the difficulty of algorithmically describing a human creative process such as evaluating and selecting significant information and composing meaningful explanations in a visually plausible manner. The project also involves experts from several disciplines including network and medical visualization, data mining, systems biology as well as perceptual psychology. The result will provide a new direction for physiological process analysis and accelerate the knowledge transfer not only within experts but also to the public. Acknowledgment: The project has received funding from the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 747985.