Information
- Publication Type: Student Project
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: 2005
- First Supervisor: Ivan Viola
Abstract
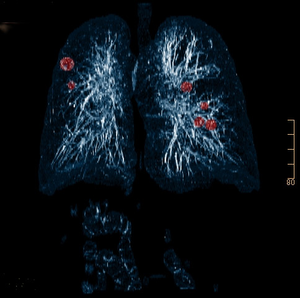
In this paper I am describing a computer aided detection (CAD) method, which is able to detect lung nodules in medical data sets. The data sets are obtained by a high resolution computer tomography. The goal of the nodule detection is to gain an early nodule detection which increases the probability of survival. Introduced method is able to detect nodules of variable size and variable shape. It is also rotation-invariant. The detection algorithm is based on the Hessian matrix. This matrix consists of the second-order partial derivatives. The eigenvalues of this matrix are used to determine the probability of a nodule-like shape. This method is well adapted to detect nodules of a size larger than 4 mm diameter. Tests with synthetic nodule data sets and some real data sets provided a high probability of true nodule detection with a very low number of false positives per data set.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@studentproject{haidacher-2005-MND,
title = "Multiscale Nodule Detection in CT Data",
author = "Martin Haidacher",
year = "2005",
abstract = "In this paper I am describing a computer aided detection
(CAD) method, which is able to detect lung nodules in
medical data sets. The data sets are obtained by a high
resolution computer tomography. The goal of the nodule
detection is to gain an early nodule detection which
increases the probability of survival. Introduced method is
able to detect nodules of variable size and variable shape.
It is also rotation-invariant. The detection algorithm is
based on the Hessian matrix. This matrix consists of the
second-order partial derivatives. The eigenvalues of this
matrix are used to determine the probability of a
nodule-like shape. This method is well adapted to detect
nodules of a size larger than 4 mm diameter. Tests with
synthetic nodule data sets and some real data sets provided
a high probability of true nodule detection with a very low
number of false positives per data set.",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2005/haidacher-2005-MND/",
}