Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: 2005
- TU Wien Library:
- First Supervisor:
Abstract
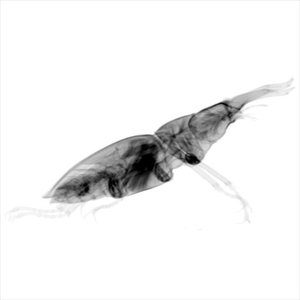
Volume rendering techniques are conventionally classified into two categories represented by direct and indirect methods. Indirect methods require to transform the initial volumetric model into an intermediate geometrical model in order to efficiently visualize it. In contrast, direct volume-rendering (DVR) methods can directly process the volumetric data. Modern 3D scanning technologies, like CT or MRI, usually provide data as a set of samples on rectilinear grid points, which are computed from the measured projections by discrete tomographic reconstruction. Therefore the set of these reconstructed samples can already be considered as an intermediate volume representation. In this diploma thesis a new paradigm for direct direct volume rendering (D2VR) is introduced, which does not even require a rectilinear grid, since it is based on an immediate processing of the measured projections. Arbitrary samples for ray casting are reconstructed from the projections by using the Filtered Back-Projection algorithm. The method presented in this thesis removes an unnecessary and lossy resampling step from the classical volume rendering pipeline. Thus, it provides much higher accuracy than traditional grid-based resampling techniques do. Furthermore a novel high-quality gradient estimation scheme, which is also based on the Filtered Back-Projection algorithm is presented. Finally we introduce a hierarchical space partitioning approach for projection-based volumetric data, which is used to accelerate D²VR.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@mastersthesis{rautek-2005-dvr,
title = "D²VR High-Quality Volume Rendering of Projection-based
Volumetric Data",
author = "Peter Rautek",
year = "2005",
abstract = "Volume rendering techniques are conventionally classified
into two categories represented by direct and indirect
methods. Indirect methods require to transform the initial
volumetric model into an intermediate geometrical model in
order to efficiently visualize it. In contrast, direct
volume-rendering (DVR) methods can directly process the
volumetric data. Modern 3D scanning technologies, like CT or
MRI, usually provide data as a set of samples on rectilinear
grid points, which are computed from the measured
projections by discrete tomographic reconstruction.
Therefore the set of these reconstructed samples can already
be considered as an intermediate volume representation. In
this diploma thesis a new paradigm for direct direct volume
rendering (D2VR) is introduced, which does not even require
a rectilinear grid, since it is based on an immediate
processing of the measured projections. Arbitrary samples
for ray casting are reconstructed from the projections by
using the Filtered Back-Projection algorithm. The method
presented in this thesis removes an unnecessary and lossy
resampling step from the classical volume rendering
pipeline. Thus, it provides much higher accuracy than
traditional grid-based resampling techniques do. Furthermore
a novel high-quality gradient estimation scheme, which is
also based on the Filtered Back-Projection algorithm is
presented. Finally we introduce a hierarchical space
partitioning approach for projection-based volumetric data,
which is used to accelerate D²VR.",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2005/rautek-2005-dvr/",
}
 PDF
PDF


