Information
- Publication Type: Technical Report
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: December 2008
- Number: TR-186-2-08-14
Abstract
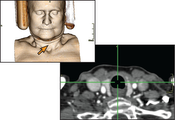
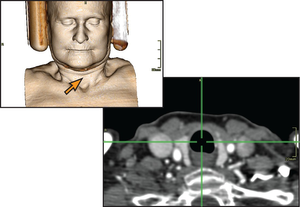
This paper presents two techniques for the linking of 2D and 3D views in medical applications. Hereby, the goal is a better integration of 3D volume visualization into the diagnostic workflow. Until now, the main obstacle for a good integration is the time-consuming process to adjust various parameters. The LiveSync interaction metaphor is a new concept to synchronize 2D slice views and 3D volumetric views of medical data sets. A single intuitive picking interaction on anatomical structures which are detected in 2D slices results in an automatically generated 3D view. To further improve the integration contextual picking is presented as a method for the interactive identification of contextual interest points within volumetric data. Our results demonstrate how these techniques improve the efficiency to generate diagnostically relevant images and how contextual interest points can, e.g., facilitate the highlighting of relevant structures.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@techreport{TR-186-2-08-14,
title = "Smart Linking of 2D and 3D Views in Medical Applications",
author = "Peter Kohlmann and Stefan Bruckner and Armin Kanitsar and
Eduard Gr\"{o}ller",
year = "2008",
abstract = "This paper presents two techniques for the linking of 2D and
3D views in medical applications. Hereby, the goal is a
better integration of 3D volume visualization into the
diagnostic workflow. Until now, the main obstacle for a good
integration is the time-consuming process to adjust various
parameters. The LiveSync interaction metaphor is a new
concept to synchronize 2D slice views and 3D volumetric
views of medical data sets. A single intuitive picking
interaction on anatomical structures which are detected in
2D slices results in an automatically generated 3D view. To
further improve the integration contextual picking is
presented as a method for the interactive identification of
contextual interest points within volumetric data. Our
results demonstrate how these techniques improve the
efficiency to generate diagnostically relevant images and
how contextual interest points can, e.g., facilitate the
highlighting of relevant structures.",
month = dec,
number = "TR-186-2-08-14",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
institution = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
note = "human contact: technical-report@cg.tuwien.ac.at",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2008/TR-186-2-08-14/",
}

 technical report
technical report