Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: July 2009
- TU Wien Library:
- Diploma Examination: 20. July 2009
- First Supervisor:
Abstract
In this work, a framework for interactive visual analysis of attributed graphs has been
developed. An attributed graph is an extension of the standard graph of a binary
relation, which attaches a set of attributes to the nodes and edges. The implemented
visual analysis techniques aim at the local level at enabling an intuitive navigation in the
graph which reveals both the structure of the selected part of the graph and the
attributes of the nodes and edges in this part. At the global level these techniques aim at
understanding the distributions of the attributes in the graph as a whole or in specific
parts in it and at spotting meaningful associations between the attributes and the
relations.
The work presents several extensions to the attributes such as graph‐theoretic features,
values aggregated over the relations, and hierarchical grouping. All attributes are
treated in a unified manner which helps performing elaborate analysis tasks using the
existing tools.
Additionally, novel graph drawing techniques are proposed. They are designed to
understand attribute distributions and associations in the graph. These techniques can
be additionally used to visualize results of queries in the data, which can be also visually
defined using the attribute analysis tools.
Finally, the work addresses several types of association analysis in relational data, along
with visual analysis methods for them. It presents a perceptual enhancement for the
well‐known parallel sets technique for association analysis in categorical data, and
proposes extensions for employing it in relational data. Also, novels methods for other
types of association analysis are introduced.
The relational data in this work were defined upon typed events in an event‐based
system, which offers a flexible architecture for real‐time analysis. Nevertheless, the
presented analysis methods are generic and have been tested on two real‐world
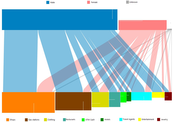
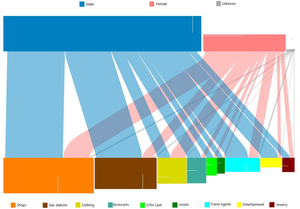
datasets. In the first dataset, entities for customers and products are derived from the
purchase events, and various meaningful associations were found between the attributes
and the relation (for example, which types of products the female customers bought
more frequently, or at which age customers have higher interest for books). In the
second dataset, events in an issue‐tracking system are analyzed to find out ticket
assignment patterns and forwarding patterns between the support offices.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
No further information available.
BibTeX
@mastersthesis{alsallakh-2009-iva,
title = "Interactive Visual Analysis of Relational Data and
Applications in Event-Based Business Analytics",
author = "Bilal Alsallakh",
year = "2009",
abstract = "In this work, a framework for interactive visual analysis of
attributed graphs has been developed. An attributed graph is
an extension of the standard graph of a binary relation,
which attaches a set of attributes to the nodes and edges.
The implemented visual analysis techniques aim at the local
level at enabling an intuitive navigation in the graph which
reveals both the structure of the selected part of the graph
and the attributes of the nodes and edges in this part. At
the global level these techniques aim at understanding the
distributions of the attributes in the graph as a whole or
in specific parts in it and at spotting meaningful
associations between the attributes and the relations. The
work presents several extensions to the attributes such as
graph‐theoretic features, values aggregated over the
relations, and hierarchical grouping. All attributes are
treated in a unified manner which helps performing elaborate
analysis tasks using the existing tools. Additionally, novel
graph drawing techniques are proposed. They are designed to
understand attribute distributions and associations in the
graph. These techniques can be additionally used to
visualize results of queries in the data, which can be also
visually defined using the attribute analysis tools.
Finally, the work addresses several types of association
analysis in relational data, along with visual analysis
methods for them. It presents a perceptual enhancement for
the well‐known parallel sets technique for association
analysis in categorical data, and proposes extensions for
employing it in relational data. Also, novels methods for
other types of association analysis are introduced. The
relational data in this work were defined upon typed events
in an event‐based system, which offers a flexible
architecture for real‐time analysis. Nevertheless, the
presented analysis methods are generic and have been tested
on two real‐world datasets. In the first dataset, entities
for customers and products are derived from the purchase
events, and various meaningful associations were found
between the attributes and the relation (for example, which
types of products the female customers bought more
frequently, or at which age customers have higher interest
for books). In the second dataset, events in an
issue‐tracking system are analyzed to find out ticket
assignment patterns and forwarding patterns between the
support offices.",
month = jul,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2009/alsallakh-2009-iva/",
}
 image
image paper
paper