Information
- Publication Type: Conference Paper
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: February 2009
- ISBN: 978-80-86943-93-0
- Location: Plzen, Tschechien
- Lecturer: Michael Glanznig
- Editor: Vaclav Skala
- Booktitle: Proceedings of the International Conference in Central Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision
- Conference date: 2. February 2009 – 5. February 2009
- Pages: 33 – 40
- Keywords: isosurface correction, iso-value field, contouring, marching cubes, blending between isosurfaces
Abstract
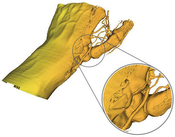
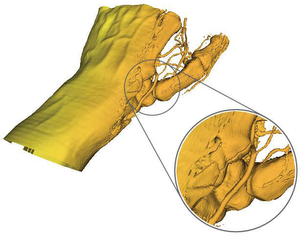
We present a locally adaptive marching cubes algorithm. It is a modification of the marching cubes algorithm where instead of a global iso-value each grid point has its own iso-value. This defines an iso-value field, which modifies the case identification process in the algorithm. The marching cubes algorithm uses linear interpolation to compute intersections of the surface with the cell edges. Our modification computes the intersection of two general line segments, because there is no longer a constant iso-value at each cube vertex. An iso-value field enables the algorithm to correct biases within the dataset like low frequency noise, contrast drifts, local density variations and other artefacts introduced by the measurement process. It can also be used for blending between different isosurfaces (e.g., skin, veins and bone in a medical dataset).Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@inproceedings{glanznig-2009-LAMC,
title = "Locally Adaptive Marching Cubes through Iso-value Variation",
author = "Michael Glanznig and Muhammad Muddassir Malik and Eduard
Gr\"{o}ller",
year = "2009",
abstract = "We present a locally adaptive marching cubes algorithm. It
is a modification of the marching cubes algorithm where
instead of a global iso-value each grid point has its own
iso-value. This defines an iso-value field, which modifies
the case identification process in the algorithm. The
marching cubes algorithm uses linear interpolation to
compute intersections of the surface with the cell edges.
Our modification computes the intersection of two general
line segments, because there is no longer a constant
iso-value at each cube vertex. An iso-value field enables
the algorithm to correct biases within the dataset like low
frequency noise, contrast drifts, local density variations
and other artefacts introduced by the measurement process.
It can also be used for blending between different
isosurfaces (e.g., skin, veins and bone in a medical
dataset).",
month = feb,
isbn = "978-80-86943-93-0",
location = "Plzen, Tschechien",
editor = "Vaclav Skala",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference in Central
Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer
Vision",
pages = "33--40",
keywords = "isosurface correction, iso-value field, contouring, marching
cubes, blending between isosurfaces",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2009/glanznig-2009-LAMC/",
}

 Full paper
Full paper