Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper (without talk)
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: November 2010
- Journal: IEEE Transactions on visualization and Computer Graphics
- Number: 6
- Volume: 16
- Booktitle: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
- Date (from): 2010
- Pages: 1458 – 1467
- Keywords: decision making, simulation steering, parallel worlds, CFD, smoothed particle hydrodynamics., Problem solving environment
Abstract
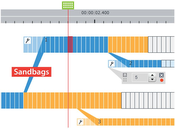
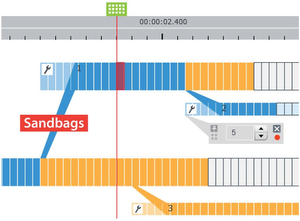
In this paper we present World Lines as a novel interactive visualization that provides complete control over multiple
heterogeneous simulation runs. In many application areas, decisions can only be made by exploring alternative scenarios. The goal
of the suggested approach is to support users in this decision making process. In this setting, the data domain is extended to a set of
alternative worlds where only one outcome will actually happen. World Lines integrates simulation, visualization and computational
steering into a single unified system that is capable of dealing with the extended solution space. World Lines represents simulation
runs as causally connected tracks that share a common time axis. This setup enables users to interfere and add new information
quickly. A World Line is introduced as a visual combination of user events and their effects in order to present a possible future. To
quickly find the most attractive outcome, we suggest World Lines as the governing component in a system of multiple linked views
and a simulation component. World Lines employs linking and brushing to enable comparative visual analysis of multiple simulations
in linked views. Analysis results can be mapped to various visual variables that World Lines provides in order to highlight the most
compelling solutions. To demonstrate this technique we present a flooding scenario and show the usefulness of the integrated
approach to support informed decision making.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{Waser-2010-WL,
title = "World Lines",
author = "J\"{u}rgen Waser and Raphael Fuchs and Hrvoje
Ribi\v{c}i\'{c} and Benjamin Schindler and G\"{u}nter
Bl\"{o}schl and Eduard Gr\"{o}ller",
year = "2010",
abstract = "In this paper we present World Lines as a novel interactive
visualization that provides complete control over multiple
heterogeneous simulation runs. In many application areas,
decisions can only be made by exploring alternative
scenarios. The goal of the suggested approach is to support
users in this decision making process. In this setting, the
data domain is extended to a set of alternative worlds where
only one outcome will actually happen. World Lines
integrates simulation, visualization and computational
steering into a single unified system that is capable of
dealing with the extended solution space. World Lines
represents simulation runs as causally connected tracks that
share a common time axis. This setup enables users to
interfere and add new information quickly. A World Line is
introduced as a visual combination of user events and their
effects in order to present a possible future. To quickly
find the most attractive outcome, we suggest World Lines as
the governing component in a system of multiple linked views
and a simulation component. World Lines employs linking and
brushing to enable comparative visual analysis of multiple
simulations in linked views. Analysis results can be mapped
to various visual variables that World Lines provides in
order to highlight the most compelling solutions. To
demonstrate this technique we present a flooding scenario
and show the usefulness of the integrated approach to
support informed decision making.",
month = nov,
journal = "IEEE Transactions on visualization and Computer Graphics",
number = "6",
volume = "16",
booktitle = "IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics",
pages = "1458--1467",
keywords = "decision making, simulation steering, parallel worlds, CFD,
smoothed particle hydrodynamics., Problem solving
environment",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2010/Waser-2010-WL/",
}

 Paper
Paper