Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: July 2010
- TU Wien Library:
- Diploma Examination: 25. July 2010
- First Supervisor:
- Milos Sramek
- Andrej Varchola
Abstract
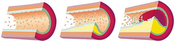
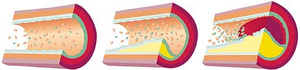
Automated processing and visualization of vascular structures is a common task in medical imaging. Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP) and Curved Planar Reformation (CPR) are well established and robust methods for clinical use. In case of calcified vessel walls, occlusion prevents exploring the inside of the vessels when using MIP. CPR allows to cut a single vessel along its centerline and to visualize the lumen. Extending the idea of CPR, a novel automatic method for vessel visualization is proposed. It works with multiple vessel centerlines that do not necessarily need to be connected into a tree structure. Arbitrarily complex vascular structures are rendered in the volume as point sets and optionally, occlusion halos are created around them to enhance depth perception. Vessel centerlines are automatically extracted from a volumetric data-set after performing feature extraction in a scale-space. The user is provided with the ability to control the final image and he or she can visually select the desired centerlines with visual queries by stroking with the mouse. Furthermore, a combination with the recent Maximum Intensity Difference Accumulation (MIDA) visualization technique is presented, which has the advantages of Direct Volume Rendering (DVR) such as occlusion and depth cues, but does not require an explicit transfer function specification. It is demonstrated how the proposed technique can be applied to large data-sets, particularly to data featuring peripheral arterial occlusive diseases or in order to detect possible embolisms as presented on a pulmonary data-set.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@mastersthesis{mistelbauer-2010-pvv,
title = "Automated Processing and Visualization of Vessel Trees",
author = "Gabriel Mistelbauer",
year = "2010",
abstract = "Automated processing and visualization of vascular
structures is a common task in medical imaging. Maximum
Intensity Projection (MIP) and Curved Planar Reformation
(CPR) are well established and robust methods for clinical
use. In case of calcified vessel walls, occlusion prevents
exploring the inside of the vessels when using MIP. CPR
allows to cut a single vessel along its centerline and to
visualize the lumen. Extending the idea of CPR, a novel
automatic method for vessel visualization is proposed. It
works with multiple vessel centerlines that do not
necessarily need to be connected into a tree structure.
Arbitrarily complex vascular structures are rendered in the
volume as point sets and optionally, occlusion halos are
created around them to enhance depth perception. Vessel
centerlines are automatically extracted from a volumetric
data-set after performing feature extraction in a
scale-space. The user is provided with the ability to
control the final image and he or she can visually select
the desired centerlines with visual queries by stroking with
the mouse. Furthermore, a combination with the recent
Maximum Intensity Difference Accumulation (MIDA)
visualization technique is presented, which has the
advantages of Direct Volume Rendering (DVR) such as
occlusion and depth cues, but does not require an explicit
transfer function specification. It is demonstrated how the
proposed technique can be applied to large data-sets,
particularly to data featuring peripheral arterial occlusive
diseases or in order to detect possible embolisms as
presented on a pulmonary data-set.",
month = jul,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2010/mistelbauer-2010-pvv/",
}
 image
image paper
paper