Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: June 2012
- Journal: Journal of WSCG
- Volume: 20
- Number: 3
- Location: Plzen, Czech Republic
- Lecturer: David Schedl
- ISSN: 1213-6972
- Event: WSCG 2012
- Conference date: 25. June 2012 – 28. June 2012
- Pages: 239 – 246
- Keywords: realtime, rendering, depth-of-field, layers, depth peeling
Abstract
Depth of field (DoF) represents a distance range around a focal plane, where objects on an image are crisp. DoF is one of the effects which significantly contributes to the photorealism of images and therefore is often simulated in rendered images. Various methods for simulating DoF have been proposed so far, but little tackle the issue of partial occlusion: Blurry objects near the camera are semi-transparent and result in partially visible background objects. This effect is strongly apparent in miniature and macro photography. In this work a DoF method is presented which simulates partial occlusion. The contribution of this work is a layered method where the scene is rendered into layers. Blurring is done efficiently with recursive Gaussian filters. Due to the usage of Gaussian filters big artifact-free blurring radii can be simulated at reasonable costs.Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
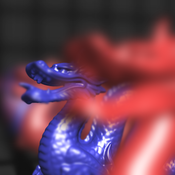 thumb:
Rendering produced with this method.
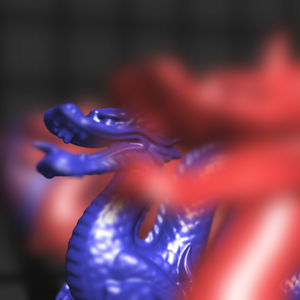
thumb:
Rendering produced with this method.
Additional files
 paper_highres:
The camera ready paper with full resolution images (21.7 MB).
paper_highres:
The camera ready paper with full resolution images (21.7 MB).
 paper:
The camera ready paper (1.18 MB).
paper:
The camera ready paper (1.18 MB).
 slides_pdf:
WSCG-slides (PDF)
slides_pdf:
WSCG-slides (PDF)
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@article{schedl-2012-dof,
title = "A layered depth-of-field method for solving partial
occlusion",
author = "David Schedl and Michael Wimmer",
year = "2012",
abstract = "Depth of field (DoF) represents a distance range around a
focal plane, where objects on an image are crisp. DoF is one
of the effects which significantly contributes to the
photorealism of images and therefore is often simulated in
rendered images. Various methods for simulating DoF have
been proposed so far, but little tackle the issue of partial
occlusion: Blurry objects near the camera are
semi-transparent and result in partially visible background
objects. This effect is strongly apparent in miniature and
macro photography. In this work a DoF method is presented
which simulates partial occlusion. The contribution of this
work is a layered method where the scene is rendered into
layers. Blurring is done efficiently with recursive Gaussian
filters. Due to the usage of Gaussian filters big
artifact-free blurring radii can be simulated at reasonable
costs.",
month = jun,
journal = "Journal of WSCG",
volume = "20",
number = "3",
issn = "1213-6972",
pages = "239--246",
keywords = "realtime, rendering, depth-of-field, layers, depth peeling",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2012/schedl-2012-dof/",
}

 paper
paper