Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: January 2014
- Date (Start): 26. June 2012
- TU Wien Library:
- Diploma Examination: 2014
- First Supervisor:
- Keywords: user guidance, annotating objects, information system
Abstract
The preservation of archaeological sites is an important task in cultural heritage. Classical methods
conserve archaeological objects in museums and provide restoration of archaeological sites
threatened by decay. The improved digitalization provides the possibility to generate an accurate
representation of archaeological sites by using laser scanners. The resulting point clouds
can preserve the archaeological site and provide the possibility to view it in its digital form even
if it no longer exists.
Usually, the archaeological site comes with a lot of different material, which has been created
over the years. This material provides information about the digitalized object, which helps to
gain a deeper understanding about the presented archaeological site.
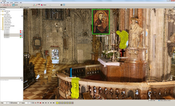
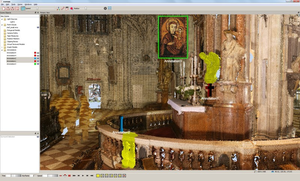
This thesis presents an annotation system for a point-cloud renderer. The system allows
adding annotations in the 3D space next to the part of the point cloud it belongs to. This helps to
provide the additional information of the point cloud in the context it belongs to. Moreover, each
annotation should present interesting information about specific annotated parts of the archaeological
site to the viewer. Besides simple textual annotations, a variable amount of documents,
such as images and PDFs, can be attached to each annotation to provide all kind of information.
Several filtering techniques, including viewpoint-dependent priority filtering, are presented
to control the visibility of the annotations. Moreover, a guidance system based on graphs is
introduced to lead viewers to different points of interest, which are represented as annotations.
To provide a clear connection between annotations and the annotated part of the point cloud,
a point-selection method and a point-marking method are presented. To allow the connection of
a large set of annotations to a single point cloud, these methods are developed in CUDA. This
is done by extending existing methods, which create octrees in CUDA. The developed methods
allow fast execution on the GPU while a CPU-based method is not able to handle such a large
amount of point selections in real-time.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
No further information available.
BibTeX
@mastersthesis{Tragust-2014-master-thesis,
title = "Integrating Annotations into a Point-based Rendering System",
author = "Markus Tragust",
year = "2014",
abstract = "The preservation of archaeological sites is an important
task in cultural heritage. Classical methods conserve
archaeological objects in museums and provide restoration of
archaeological sites threatened by decay. The improved
digitalization provides the possibility to generate an
accurate representation of archaeological sites by using
laser scanners. The resulting point clouds can preserve the
archaeological site and provide the possibility to view it
in its digital form even if it no longer exists. Usually,
the archaeological site comes with a lot of different
material, which has been created over the years. This
material provides information about the digitalized object,
which helps to gain a deeper understanding about the
presented archaeological site. This thesis presents an
annotation system for a point-cloud renderer. The system
allows adding annotations in the 3D space next to the part
of the point cloud it belongs to. This helps to provide the
additional information of the point cloud in the context it
belongs to. Moreover, each annotation should present
interesting information about specific annotated parts of
the archaeological site to the viewer. Besides simple
textual annotations, a variable amount of documents, such as
images and PDFs, can be attached to each annotation to
provide all kind of information. Several filtering
techniques, including viewpoint-dependent priority
filtering, are presented to control the visibility of the
annotations. Moreover, a guidance system based on graphs is
introduced to lead viewers to different points of interest,
which are represented as annotations. To provide a clear
connection between annotations and the annotated part of the
point cloud, a point-selection method and a point-marking
method are presented. To allow the connection of a large set
of annotations to a single point cloud, these methods are
developed in CUDA. This is done by extending existing
methods, which create octrees in CUDA. The developed methods
allow fast execution on the GPU while a CPU-based method is
not able to handle such a large amount of point selections
in real-time.",
month = jan,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
keywords = "user guidance, annotating objects, information system",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2014/Tragust-2014-master-thesis/",
}
 thesis
thesis