Information
- Publication Type: Conference Paper
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: February 2015
- ISBN: 978-1-4503-3392-4
- Publisher: ACM
- Organization: ACM
- Location: San Francisco, CA
- Lecturer: Thomas Weber
- Booktitle: Proceedings of the 19th Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games (i3D 2015)
- Conference date: 27. February 2015 – 1. March 2015
- Pages: 39 – 45
- Keywords: micro-rasterization
Abstract
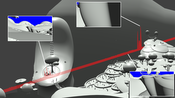
Recent advances in graphics hardware have made it a desirable goal to implement the Reyes algorithm on current graphics cards. One key component in this algorithm is the bound-and-split phase, where surface patches are recursively split until they are smaller than a given screen-space bound. While this operation has been successfully parallelized for execution on the GPU using a breadth-first traversal, the resulting implementations are limited by their unpredictable worst-case memory consumption and high global memory bandwidth utilization. In this paper, we propose an alternate strategy that allows limiting the amount of necessary memory by controlling the number of assigned worker threads. The result is an implementation that scales to the performance of the breadth-first approach while offering three advantages: significantly decreased memory usage, a smooth and predictable tradeoff between memory usage and performance, and increased locality for surface processing. This allows us to render scenes that would require too much memory to be processed by the breadth-first method.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@inproceedings{WEBER-2015-PRA,
title = "Parallel Reyes-style Adaptive Subdivision with Bounded
Memory Usage",
author = "Thomas Weber and Michael Wimmer and John Owens",
year = "2015",
abstract = "Recent advances in graphics hardware have made it a
desirable goal to implement the Reyes algorithm on current
graphics cards. One key component in this algorithm is the
bound-and-split phase, where surface patches are recursively
split until they are smaller than a given screen-space
bound. While this operation has been successfully
parallelized for execution on the GPU using a breadth-first
traversal, the resulting implementations are limited by
their unpredictable worst-case memory consumption and high
global memory bandwidth utilization. In this paper, we
propose an alternate strategy that allows limiting the
amount of necessary memory by controlling the number of
assigned worker threads. The result is an implementation
that scales to the performance of the breadth-first approach
while offering three advantages: significantly decreased
memory usage, a smooth and predictable tradeoff between
memory usage and performance, and increased locality for
surface processing. This allows us to render scenes that
would require too much memory to be processed by the
breadth-first method.",
month = feb,
isbn = "978-1-4503-3392-4",
publisher = "ACM",
organization = "ACM",
location = "San Francisco, CA",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 19th Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics
and Games (i3D 2015)",
pages = "39--45",
keywords = "micro-rasterization",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2015/WEBER-2015-PRA/",
}
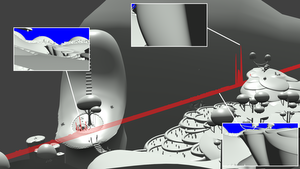

 draft
draft