Information
- Publication Type: Bachelor Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: June 2016
- Date (Start): February 2016
- Date (End): June 2016
- Matrikelnummer: 1128636
- First Supervisor: Eduard Gröller
Abstract
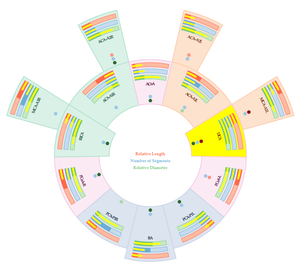
The human brain is supplied with blood by arteries that form a collateral circulation, the so-called Circle of Willis (CoW). The anatomy of the CoW varies considerably among the population. In fact, depending on the study, just 13% to 72% of the population does have the typical textbook illustration of the CoW. Although divergent configurations are usually not pathological, some incomplete configurations increase the risk of stroke. Furthermore, studies suggest an association between certain neurological diseases and abnormal configurations of the CoW. Thus, for the diagnosis and treatment of diverse neurological diseases the assessment of the patient’s CoW is an important issue. This thesis addresses the development of a software for a comparative visualization of the CoWs of a population with the CoWs of a second population. For this purpose, an average CoW is calculated for each of the populations. The two resulting CoWs are then visualized side-by-side, so that the viewer is able to distinguish differences between the CoWs of the two populations with relatively little effort. The aim of this visualization is the support of studies that consider the clinical significance of the different CoW configurations as well as the support of diagnosis and treatment of diseases that are caused by an abnormal configuration of the CoW. The latter can be achieved by comparing the patient’s CoW with datasets of risk groups or with a dataset of a healthy population.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@bachelorsthesis{Gadllah_Hani_2016,
title = "Comparative Visualization of the Circle of Willis",
author = "Hani Gadllah",
year = "2016",
abstract = "The human brain is supplied with blood by arteries that form
a collateral circulation, the so-called Circle of Willis
(CoW). The anatomy of the CoW varies considerably among the
population. In fact, depending on the study, just 13% to 72%
of the population does have the typical textbook
illustration of the CoW. Although divergent configurations
are usually not pathological, some incomplete configurations
increase the risk of stroke. Furthermore, studies suggest an
association between certain neurological diseases and
abnormal configurations of the CoW. Thus, for the diagnosis
and treatment of diverse neurological diseases the
assessment of the patient’s CoW is an important issue.
This thesis addresses the development of a software for a
comparative visualization of the CoWs of a population with
the CoWs of a second population. For this purpose, an
average CoW is calculated for each of the populations. The
two resulting CoWs are then visualized side-by-side, so that
the viewer is able to distinguish differences between the
CoWs of the two populations with relatively little effort.
The aim of this visualization is the support of studies that
consider the clinical significance of the different CoW
configurations as well as the support of diagnosis and
treatment of diseases that are caused by an abnormal
configuration of the CoW. The latter can be achieved by
comparing the patient’s CoW with datasets of risk groups
or with a dataset of a healthy population. ",
month = jun,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2016/Gadllah_Hani_2016/",
}
 image
image

