Information
- Publication Type: Bachelor Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: March 2017
- Date (Start): 1. October 2016
- Date (End): 8. March 2017
- Matrikelnummer: 1225540
- First Supervisor: Eduard Gröller
Abstract
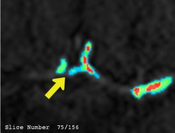
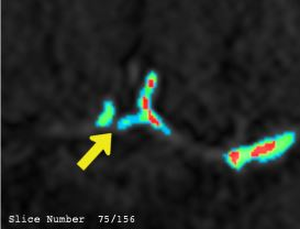
Image segmentation is an important processing step in various applications and crucial in the medical field. When a new segmentation technique is introduced, validation and evaluation are essential for medical image analysis. But the automation of these processes is still not sufficient. Many algorithms have been published but there is still no satisfying way to assess whether an algorithm produces more accurate segmentations than another. More effort is spent on the development of algorithms than on their evaluation and therefore many researchers use the less complex subjective methods. For these techniques multiple experts are needed to visually compare several segmentation results, which is a very time-consuming process. Another way of comparing different results is the supervised evaluation method. Here we need experts, who manually segment reference images, which are used for comparison. As seen in recent researches there is a need for unsupervised methods due to many applications, in which user assistance is infeasible. The aim of this thesis is to provide an environment to visually and objectively evaluate segmentation results in the field of vessel segmentations. Our framework enables the comparison at voxel-level with various visualization techniques and objective measurements. These methods are meant to make the comparison more understandable for users. A subjective evaluation is realized through a comparative visualization by using a two- and three-dimensional comparison of voxels. Another general overview is provided by a maximum-intensity projection, which highlights the vessel structure. As purely objective evaluation technique, various metrics are used, to assure independence from experts or a ground truth. By using these techniques this paper presents an approach for evaluating differences in medical images, which does not rely on a permanent presence of an expert.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@bachelorsthesis{Gall_2017,
title = "Comparison of Vessel Segmentation Techniques",
author = "Alexander Gall",
year = "2017",
abstract = "Image segmentation is an important processing step in
various applications and crucial in the medical field. When
a new segmentation technique is introduced, validation and
evaluation are essential for medical image analysis. But the
automation of these processes is still not sufficient. Many
algorithms have been published but there is still no
satisfying way to assess whether an algorithm produces more
accurate segmentations than another. More effort is spent on
the development of algorithms than on their evaluation and
therefore many researchers use the less complex subjective
methods. For these techniques multiple experts are needed to
visually compare several segmentation results, which is a
very time-consuming process. Another way of comparing
different results is the supervised evaluation method. Here
we need experts, who manually segment reference images,
which are used for comparison. As seen in recent researches
there is a need for unsupervised methods due to many
applications, in which user assistance is infeasible. The
aim of this thesis is to provide an environment to visually
and objectively evaluate segmentation results in the field
of vessel segmentations. Our framework enables the
comparison at voxel-level with various visualization
techniques and objective measurements. These methods are
meant to make the comparison more understandable for users.
A subjective evaluation is realized through a comparative
visualization by using a two- and three-dimensional
comparison of voxels. Another general overview is provided
by a maximum-intensity projection, which highlights the
vessel structure. As purely objective evaluation technique,
various metrics are used, to assure independence from
experts or a ground truth. By using these techniques this
paper presents an approach for evaluating differences in
medical images, which does not rely on a permanent presence
of an expert.",
month = mar,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2017/Gall_2017/",
}
 Bachelor Thesis
Bachelor Thesis image
image