Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper (without talk)
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: October 2017
- ISSN: 0097-8493
- Journal: Computers & Graphics
- Volume: 67
- Pages: 1 – 13
- Keywords: tree modeling, LIDAR, point clouds
Abstract
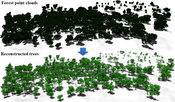
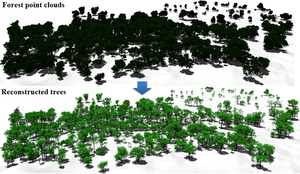
Modeling real-world trees is important in many application areas, including computer graphics, botany and forestry. An example of a modeling method is reconstruction from light detection and ranging (LiDAR) scans. In contrast to terrestrial LiDAR systems, airborne LiDAR systems – even current high-resolution systems – capture only very few samples on tree branches, which makes the reconstruction of trees from airborne LiDAR a challenging task. In this paper, we present a new method to model plausible trees with fine details from airborne LiDAR point clouds. To reconstruct tree models, first, we use a normalized cut method to segment an individual tree point cloud. Then, trunk points are added to supplement the incomplete point cloud, and a connected graph is constructed by searching sufficient nearest neighbors for each point. Based on the observation of real-world trees, a direction field is created to restrict branch directions. Then, branch skeletons are constructed using a bottom-up greedy algorithm with a priority queue, and leaves are arranged according to phyllotaxis. We demonstrate our method on a variety of examples and show that it can generate a plausible tree model in less than one second, in addition to preserving features of the original point cloud.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
No further information available.
BibTeX
@article{HU-2017-ETM,
title = "Efficient Tree Modeling from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds",
author = "Shaojun Hu and Zhengrong Li and Zhiyi Zhang and Dongijan He
and Michael Wimmer",
year = "2017",
abstract = "Modeling real-world trees is important in many application
areas, including computer graphics, botany and forestry. An
example of a modeling method is reconstruction from light
detection and ranging (LiDAR) scans. In contrast to
terrestrial LiDAR systems, airborne LiDAR systems – even
current high-resolution systems – capture only very few
samples on tree branches, which makes the reconstruction of
trees from airborne LiDAR a challenging task. In this paper,
we present a new method to model plausible trees with fine
details from airborne LiDAR point clouds. To reconstruct
tree models, first, we use a normalized cut method to
segment an individual tree point cloud. Then, trunk points
are added to supplement the incomplete point cloud, and a
connected graph is constructed by searching sufficient
nearest neighbors for each point. Based on the observation
of real-world trees, a direction field is created to
restrict branch directions. Then, branch skeletons are
constructed using a bottom-up greedy algorithm with a
priority queue, and leaves are arranged according to
phyllotaxis. We demonstrate our method on a variety of
examples and show that it can generate a plausible tree
model in less than one second, in addition to preserving
features of the original point cloud.",
month = oct,
issn = "0097-8493",
journal = "Computers & Graphics",
volume = "67",
pages = "1--13",
keywords = "tree modeling, LIDAR, point clouds",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2017/HU-2017-ETM/",
}

 draft
draft