Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: May 2018
- Date (Start): July 2017
- Date (End): 30. May 2018
- TU Wien Library:
- Open Access: yes
- First Supervisor:
Abstract
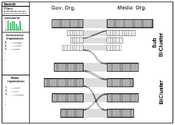
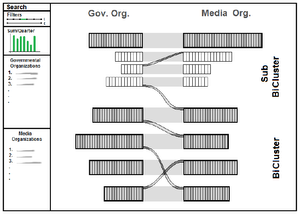
In this thesis we introduce BiCFlows, a novel interactive visualization approach to explore large bipartite graphs. We were motivated by the Media Transparency Database, a public database established by the Austrian government to provide information about governmental advertising and subsidies expenses, which holds the characteristics of a large, weighted bipartite graph. Current approaches that deal with the visualization of the Media Transparency Database are limited by the fact that they do not offer a sufficient overview of the whole dataset. Other existing approaches that are not particularly designed for the Media Transparency Database, but deal with the visualization of bipartite graphs are in addition limited by their lack of scalability for large datasets. Aggregation is an often used concept in reducing the amount of data by grouping together similar data objects. This only works if the appropriate object properties are present in the data to use them for the aggregation. If this additional information is missing, like in the Media Transparency Database, other aggregation techniques have to be used. Since we are dealing with bipartite graphs in our approach, we use the concept of biclustering to establish a hierarchical structure within the data that can be interactively explored by the user. We showed that BiCFlows cannot only be used for the Media Transparency Database, but also for other datasets that share the characteristics of a weighted bipartite graph. Furthermore, we conducted an insight-based user study to compare BiCFlows with existing concepts and discussed advantages and drawbacks. We showed that BiCFlows supported users in their exploration process and let them gain more insight than with existing approaches.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@mastersthesis{steinboeck-2017-vbn,
title = "Interactive Visual Exploration Interface for Large Bipartite
Networks",
author = "Daniel Steinb\"{o}ck",
year = "2018",
abstract = "In this thesis we introduce BiCFlows, a novel interactive
visualization approach to explore large bipartite graphs. We
were motivated by the Media Transparency Database, a public
database established by the Austrian government to provide
information about governmental advertising and subsidies
expenses, which holds the characteristics of a large,
weighted bipartite graph. Current approaches that deal with
the visualization of the Media Transparency Database are
limited by the fact that they do not offer a sufficient
overview of the whole dataset. Other existing approaches
that are not particularly designed for the Media
Transparency Database, but deal with the visualization of
bipartite graphs are in addition limited by their lack of
scalability for large datasets. Aggregation is an often used
concept in reducing the amount of data by grouping together
similar data objects. This only works if the appropriate
object properties are present in the data to use them for
the aggregation. If this additional information is missing,
like in the Media Transparency Database, other aggregation
techniques have to be used. Since we are dealing with
bipartite graphs in our approach, we use the concept of
biclustering to establish a hierarchical structure within
the data that can be interactively explored by the user. We
showed that BiCFlows cannot only be used for the Media
Transparency Database, but also for other datasets that
share the characteristics of a weighted bipartite graph.
Furthermore, we conducted an insight-based user study to
compare BiCFlows with existing concepts and discussed
advantages and drawbacks. We showed that BiCFlows supported
users in their exploration process and let them gain more
insight than with existing approaches.",
month = may,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2018/steinboeck-2017-vbn/",
}
 Master Thesis
Master Thesis Poster
Poster sketch
sketch