Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: June 2019
- Journal: Computer Graphics Forum
- Volume: 38
- Number: 3
- Location: Porto, Portugal
- Lecturer: Daniel Cornel
- ISSN: 1467-8659
- Event: Eurographics/VGTC Conference on Visualization (EuroVis) 2019
- DOI: 10.1111/cgf.13669
- Call for Papers: Call for Paper
- Conference date: 3. June 2019 – 7. June 2019
- Pages: 25 – 39
Abstract
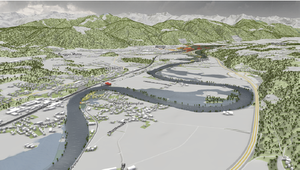
In this paper, we present a real-time technique to visualize large-scale adaptive height fields withC1-continuous surfacereconstruction. Grid-based shallow water simulation is an indispensable tool for interactive flood management applications.Height fields defined on adaptive grids are often the only viable option to store and process the massive simulation data. Theirvisualization requires the reconstruction of a continuous surface from the spatially discrete simulation data. For regular grids,fast linear and cubic interpolation are commonly used for surface reconstruction. For adaptive grids, however, there exists nohigher-order interpolation technique fast enough for interactive applications.Our proposed technique bridges the gap between fast linear and expensive higher-order interpolation for adaptive surfacereconstruction. During reconstruction, no matter if regular or adaptive, discretization and interpolation artifacts can occur,which domain experts consider misleading and unaesthetic. We take into account boundary conditions to eliminate these artifacts,which include water climbing uphill, diving towards walls, and leaking through thin objects. We apply realistic water shadingwith visual cues for depth perception and add waves and foam synthesized from the simulation data to emphasize flow directions.The versatility and performance of our technique are demonstrated in various real-world scenarios. A survey conducted withdomain experts of different backgrounds and concerned citizens proves the usefulness and effectiveness of our technique.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{CORNEL-2019-IVF,
title = "Interactive Visualization of Flood and Heavy Rain
Simulations",
author = "Daniel Cornel and Andreas Buttinger-Kreuzhuber and Artem
Konev and Zsolt Horvath and Michael Wimmer and Raimund
Heidrich and J\"{u}rgen Waser",
year = "2019",
abstract = "In this paper, we present a real-time technique to visualize
large-scale adaptive height fields withC1-continuous
surfacereconstruction. Grid-based shallow water simulation
is an indispensable tool for interactive flood management
applications.Height fields defined on adaptive grids are
often the only viable option to store and process the
massive simulation data. Theirvisualization requires the
reconstruction of a continuous surface from the spatially
discrete simulation data. For regular grids,fast linear and
cubic interpolation are commonly used for surface
reconstruction. For adaptive grids, however, there exists
nohigher-order interpolation technique fast enough for
interactive applications.Our proposed technique bridges the
gap between fast linear and expensive higher-order
interpolation for adaptive surfacereconstruction. During
reconstruction, no matter if regular or adaptive,
discretization and interpolation artifacts can occur,which
domain experts consider misleading and unaesthetic. We take
into account boundary conditions to eliminate these
artifacts,which include water climbing uphill, diving
towards walls, and leaking through thin objects. We apply
realistic water shadingwith visual cues for depth perception
and add waves and foam synthesized from the simulation data
to emphasize flow directions.The versatility and performance
of our technique are demonstrated in various real-world
scenarios. A survey conducted withdomain experts of
different backgrounds and concerned citizens proves the
usefulness and effectiveness of our technique.",
month = jun,
journal = "Computer Graphics Forum",
volume = "38",
number = "3",
issn = "1467-8659",
doi = "10.1111/cgf.13669",
pages = "25--39",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2019/CORNEL-2019-IVF/",
}

 image
image
