Information
- Publication Type: Bachelor Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: October 2019
- Date (Start): 5. March 2019
- Date (End): 15. October 2019
- Matrikelnummer: 01526772
- First Supervisor: Hsiang-Yun Wu
- Keywords: Biological pathways
Abstract
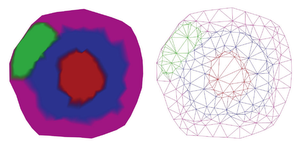
The visualization of networks for protein interactions is an important step to understand them. There are already many approaches for this task, but most of them do not show any information about the compartment of the cell the proteins belong to. Since the placement of proteins inside a cell is important information, because it helps to understand their interactions, this thesis proposes a method to visualize protein inside cell compartments. The objective of this project is a clear and understandable visualization of interactions between proteins and where these interactions or reactions happen inside the cell. This project uses a three-dimensional model of a cell as a base and intersects it using cutting planes. Then the intersection surface is sampled and reconstructed using Delaunay triangulation. To the mesh created by the triangulation, a force-directed algorithm is applied. This algorithm is used to scale single-cell parts in order to fit all proteins inside. This ensures that none of the cell parts get overfilled. The result is a new method that makes it possible to visualize not only protein-protein interactions but also in which compartment of the cell the proteins are located.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@bachelorsthesis{rinortner_susanne-2019-vpicc,
title = "Visualizing Protein Interactions in Corresponding
Compartments",
author = "Susanne Rinortner",
year = "2019",
abstract = "The visualization of networks for protein interactions is an
important step to understand them. There are already many
approaches for this task, but most of them do not show any
information about the compartment of the cell the proteins
belong to. Since the placement of proteins inside a cell is
important information, because it helps to understand their
interactions, this thesis proposes a method to visualize
protein inside cell compartments. The objective of this
project is a clear and understandable visualization of
interactions between proteins and where these interactions
or reactions happen inside the cell. This project uses a
three-dimensional model of a cell as a base and intersects
it using cutting planes. Then the intersection surface is
sampled and reconstructed using Delaunay triangulation. To
the mesh created by the triangulation, a force-directed
algorithm is applied. This algorithm is used to scale
single-cell parts in order to fit all proteins inside. This
ensures that none of the cell parts get overfilled. The
result is a new method that makes it possible to visualize
not only protein-protein interactions but also in which
compartment of the cell the proteins are located.",
month = oct,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Research Unit of Computer Graphics, Institute of Visual
Computing and Human-Centered Technology, Faculty of
Informatics, TU Wien ",
keywords = "Biological pathways",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2019/rinortner_susanne-2019-vpicc/",
}