Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: October 2019
- Journal: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
- Volume: 26
- Location: Vancouver, Canada
- Lecturer: Manuela Waldner
- Event: IEEE VIS InfoVis
- DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2019.2934784
- Call for Papers: Call for Paper
- Conference date: 20. October 2019 – 25. October 2019
- Pages: 1033 – 1042
- Keywords: radial charts, time series data, daily patterns, crowd-sourced experiment
Abstract
Radial charts are generally considered less effective than linear charts. Perhaps the only exception is in visualizing periodical time-dependent data, which is believed to be naturally supported by the radial layout. It has been demonstrated that the drawbacks of radial charts outweigh the benefits of this natural mapping. Visualization of daily patterns, as a special case, has not been systematically evaluated using radial charts. In contrast to yearly or weekly recurrent trends, the analysis of daily patterns on a radial chart may benefit from our trained skill on reading radial clocks that are ubiquitous in our culture. In a crowd-sourced experiment with 92 non-expert users, we evaluated the accuracy, efficiency, and subjective ratings of radial and linear charts for visualizing daily traffic accident patterns. We systematically compared juxtaposed 12-hours variants and single 24-hours variants for both layouts in four low-level tasks and one high-level interpretation task. Our results show that over all tasks, the most elementary 24-hours linear bar chart is most accurate and efficient and is also preferred by the users. This provides strong evidence for the use of linear layouts – even for visualizing periodical daily patterns.Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
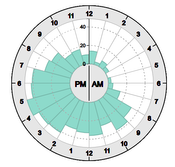 teaser:
Daily patterns visualized in a 24-hours radial chart.
teaser:
Daily patterns visualized in a 24-hours radial chart.
Additional files
 slides :
Powerpoint slides of presentation at IEEE VIS 2019 (do not contain animations and videos).
slides :
Powerpoint slides of presentation at IEEE VIS 2019 (do not contain animations and videos).
 supplement:
Supplemental information about the user study
supplement:
Supplemental information about the user study
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{waldner-2019-rld,
title = "A Comparison of Radial and Linear Charts for Visualizing
Daily Patterns",
author = "Manuela Waldner and Alexandra Diehl and Denis Gracanin and
Rainer Splechtna and Claudio Delrieux and Kresimir Matkovic",
year = "2019",
abstract = "Radial charts are generally considered less effective than
linear charts. Perhaps the only exception is in visualizing
periodical time-dependent data, which is believed to be
naturally supported by the radial layout. It has been
demonstrated that the drawbacks of radial charts outweigh
the benefits of this natural mapping. Visualization of daily
patterns, as a special case, has not been systematically
evaluated using radial charts. In contrast to yearly or
weekly recurrent trends, the analysis of daily patterns on a
radial chart may benefit from our trained skill on reading
radial clocks that are ubiquitous in our culture. In a
crowd-sourced experiment with 92 non-expert users, we
evaluated the accuracy, efficiency, and subjective ratings
of radial and linear charts for visualizing daily traffic
accident patterns. We systematically compared juxtaposed
12-hours variants and single 24-hours variants for both
layouts in four low-level tasks and one high-level
interpretation task. Our results show that over all tasks,
the most elementary 24-hours linear bar chart is most
accurate and efficient and is also preferred by the users.
This provides strong evidence for the use of linear layouts
– even for visualizing periodical daily patterns.",
month = oct,
journal = "IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics",
volume = "26",
doi = "10.1109/TVCG.2019.2934784",
pages = "1033--1042",
keywords = "radial charts, time series data, daily patterns,
crowd-sourced experiment",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2019/waldner-2019-rld/",
}

 paper
paper