Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: November 2020
- Journal: Computer Graphics Forum
- Volume: 39
- Open Access: yes
- Number: 7
- Location: Wellington, NZ
- Lecturer: Markus Schütz
- ISSN: 1467-8659
- Event: Pacific Graphics 2020
- DOI: 10.1111/cgf.14134
- Call for Papers: Call for Paper
- Pages: 13
- Publisher: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Conference date: 2021
- Pages: 1 – 13
- Keywords: point clouds, point-based rendering, level of detail
Abstract
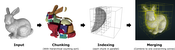
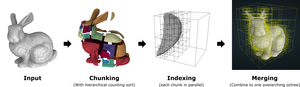
We propose an efficient out-of-core octree generation method for arbitrarily large point clouds. It utilizes a hierarchical counting sort to quickly split the point cloud into small chunks, which are then processed in parallel. Levels of detail are generated by subsampling the full data set bottom up using one of multiple exchangeable sampling strategies. We introduce a fast hierarchical approximate blue-noise strategy and compare it to a uniform random sampling strategy. The throughput, including out-of-core access to disk, generating the octree, and writing the final result to disk, is about an order of magnitude faster than the state of the art, and reaches up to around 6 million points per second for the blue-noise approach and up to around 9 million points per second for the uniform random approach on modern SSDs.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
- PotreeConverter 2.0 at github
PotreeConverter generates an octree LOD structure for streaming and real-time rendering of massive point clouds. The results can be viewed in web browsers with Potree or as a desktop application with PotreeDesktop.
- Video
- Entry in reposiTUm (TU Wien Publication Database)
- DOI: 10.1111/cgf.14134
BibTeX
@article{SCHUETZ-2020-MPC,
title = "Fast Out-of-Core Octree Generation for Massive Point Clouds",
author = "Markus Sch\"{u}tz and Stefan Ohrhallinger and Michael Wimmer",
year = "2020",
abstract = "We propose an efficient out-of-core octree generation method
for arbitrarily large point clouds. It utilizes a
hierarchical counting sort to quickly split the point cloud
into small chunks, which are then processed in parallel.
Levels of detail are generated by subsampling the full data
set bottom up using one of multiple exchangeable sampling
strategies. We introduce a fast hierarchical approximate
blue-noise strategy and compare it to a uniform random
sampling strategy. The throughput, including out-of-core
access to disk, generating the octree, and writing the final
result to disk, is about an order of magnitude faster than
the state of the art, and reaches up to around 6 million
points per second for the blue-noise approach and up to
around 9 million points per second for the uniform random
approach on modern SSDs.",
month = nov,
journal = "Computer Graphics Forum",
volume = "39",
number = "7",
issn = "1467-8659",
doi = "10.1111/cgf.14134",
pages = "13",
publisher = "John Wiley & Sons, Inc.",
pages = "1--13",
keywords = "point clouds, point-based rendering, level of detail",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2020/SCHUETZ-2020-MPC/",
}

 paper
paper