Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper (without talk)
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: April 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cola.2020.100959
- Journal: Journal of Computer Languages
- Volume: 57
- Keywords: Information visualization, Bipartite graphs, Clustering, Time series data, Insight-based evaluation
Abstract
Bipartite graphs are typically visualized using linked lists or matrices, but these visualizations neither scale well nor do they convey temporal development. We present a new interactive exploration interface for large, time-dependent bipartite graphs. We use two clustering techniques to build a hierarchical aggregation supporting different exploration strategies. Aggregated nodes and edges are visualized as linked lists with nested time series. We demonstrate two use cases: finding advertising expenses of public authorities following similar temporal patterns and comparing author-keyword co-occurrences across time. Through a user study, we show that linked lists with hierarchical aggregation lead to more insights than without.Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
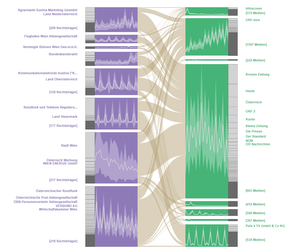
 teaser:
Dynamic BicFlows with nested time series visualization per cluster per set.
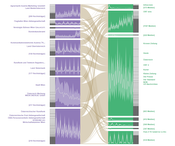
teaser:
Dynamic BicFlows with nested time series visualization per cluster per set.
Additional files
Weblinks
- paper
Open Access article at ScienceDirect - Entry in reposiTUm (TU Wien Publication Database)
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cola.2020.100959
BibTeX
@article{waldner-2020-tbg,
title = "Interactive exploration of large time-dependent bipartite
graphs",
author = "Manuela Waldner and Daniel Steinb\"{o}ck and Eduard
Gr\"{o}ller",
year = "2020",
abstract = "Bipartite graphs are typically visualized using linked lists
or matrices, but these visualizations neither scale well nor
do they convey temporal development. We present a new
interactive exploration interface for large, time-dependent
bipartite graphs. We use two clustering techniques to build
a hierarchical aggregation supporting different exploration
strategies. Aggregated nodes and edges are visualized as
linked lists with nested time series. We demonstrate two use
cases: finding advertising expenses of public authorities
following similar temporal patterns and comparing
author-keyword co-occurrences across time. Through a user
study, we show that linked lists with hierarchical
aggregation lead to more insights than without.",
month = apr,
doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cola.2020.100959",
journal = "Journal of Computer Languages",
volume = "57",
keywords = "Information visualization, Bipartite graphs, Clustering,
Time series data, Insight-based evaluation",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2020/waldner-2020-tbg/",
}