Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: March 2021
- Date (Start): 1. March 2020
- Date (End): 9. March 2021
- TU Wien Library:
- Diploma Examination: 9. March 2021
- Open Access: yes
- First Supervisor: Michael Wimmer
- Pages: 89
- Keywords: visibitility culling, ray tracing
Abstract
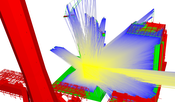
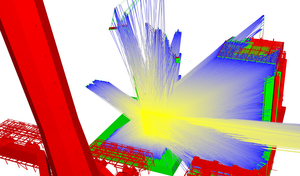
Visibility computation is a common problem in the field of computer graphics. Examples include occlusion culling, where parts of the scene are culled away, or global illumination simulations, which are based on the mutual visibility of pairs of points to calculate lighting. In this thesis, an aggressive from-region visibility technique called Guided Visibility Sampling++ (GVS++) is presented. The proposed technique improves the Guided Visibility Sampling algorithm through improved sampling strategies, thus achieving low error rates on various scenes, and being over four orders of magnitude faster than the original CPU-based Guided Visibility Sampling implementation. We present intelligent sampling strategies that use ray casting to determine a set of triangles visible from a flat or volumetric rectangular region in space. This set is called a potentially visible set (PVS). Based on initial random sampling, subsequent exploration phases progressively grow an intermediate solution. A termination criterion is used to terminate the PVS search. A modern implementation using the Vulkan graphics API and RTX ray tracing is discussed. Furthermore, optimizations are shown that allow for an implementation that is over 20 times faster than a naive implementation.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
- publication
i3D paper from the thesis - Entry in reposiTUm (TU Wien Publication Database)
- DOI: 10.34726/hss.2021.79729
BibTeX
@mastersthesis{KOCH-2021-GVSDA,
title = "Visibility precomputation with RTX ray tracing",
author = "Thomas Bernhard Koch",
year = "2021",
abstract = "Visibility computation is a common problem in the field of
computer graphics. Examples include occlusion culling, where
parts of the scene are culled away, or global illumination
simulations, which are based on the mutual visibility of
pairs of points to calculate lighting. In this thesis, an
aggressive from-region visibility technique called Guided
Visibility Sampling++ (GVS++) is presented. The proposed
technique improves the Guided Visibility Sampling algorithm
through improved sampling strategies, thus achieving low
error rates on various scenes, and being over four orders of
magnitude faster than the original CPU-based Guided
Visibility Sampling implementation. We present intelligent
sampling strategies that use ray casting to determine a set
of triangles visible from a flat or volumetric rectangular
region in space. This set is called a potentially visible
set (PVS). Based on initial random sampling, subsequent
exploration phases progressively grow an intermediate
solution. A termination criterion is used to terminate the
PVS search. A modern implementation using the Vulkan
graphics API and RTX ray tracing is discussed. Furthermore,
optimizations are shown that allow for an implementation
that is over 20 times faster than a naive implementation.",
month = mar,
pages = "89",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Research Unit of Computer Graphics, Institute of Visual
Computing and Human-Centered Technology, Faculty of
Informatics, TU Wien",
keywords = "visibitility culling, ray tracing",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2021/KOCH-2021-GVSDA/",
}
 poster
poster thesis
thesis