Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: October 2021
- Date (Start): 5. January 2021
- Date (End): 12. October 2021
- TU Wien Library:
- Diploma Examination: 12. October 2021
- Open Access: yes
- First Supervisor: Kresimir Matkovic

- Pages: 60
- Keywords: visual analytics, interactive visual analysis, machine learning, linear regression, elastic net, K-Means, classification, spatial time series, economic recession, recession factors
Abstract
Regardless of what algorithms and technologies are developed, the human mind and logical reasoning remain important tools for analysing, modelling, and solving problems. Visual representation of data is considered the most e˙ective way to convey information to the human brain and promote analytical thinking. Visual analytics encompasses a set of techniques, methods, and tools that support analytical thinking through visual representations of various types of data. Due to their complexity and size, spatial time series data are suitable for implementation of such techniques, as their analysis remains challenging. Many environmental, social, and economic processes of modern civilization are represented by spatial time series, which emphasises the need for interactive visual representations for their more eÿcient analysis.
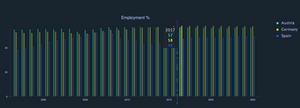
One clear example of such complex processes is economic recession, a decline in economic activity for which there is no single formal definition. However, it is often described in terms of recession factors such as GDP, the Gini index, or inflation, all of which are examples of spatial time series data, and whose change can be a clear indicator of the state of the economy. As recession analysis is a very complex topic and it is not entirely clear which economic factors have the greatest impact, purely automated techniques are not appropriate and there is scope for advances in analytical approaches.
This thesis proposes an application “Recession Explorer”: visual analytics of economic recession and its forecasting as an example of a holistic system that displays spatial time series data and explores patterns and insights in the data. Such a combination of approaches provides a unique perspective on economic recession studies by facilitating both high-level human reasoning and the use of advanced mathematical algorithms. The goal of the application is to demonstrate that the use of visual analytics is a beneficial approach to address the challenges of economic recession and, more generally, to assist users with interactive visualisations when dealing with and analysing spatial time series data.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
BibTeX
@mastersthesis{Priselac2021,
title = "Visual Analytics of Spatial Time Series Data",
author = "Marija Priselac",
year = "2021",
abstract = "Regardless of what algorithms and technologies are
developed, the human mind and logical reasoning remain
important tools for analysing, modelling, and solving
problems. Visual representation of data is considered the
most e˙ective way to convey information to the human brain
and promote analytical thinking. Visual analytics
encompasses a set of techniques, methods, and tools that
support analytical thinking through visual representations
of various types of data. Due to their complexity and size,
spatial time series data are suitable for implementation of
such techniques, as their analysis remains challenging. Many
environmental, social, and economic processes of modern
civilization are represented by spatial time series, which
emphasises the need for interactive visual representations
for their more eÿcient analysis. One clear example of such
complex processes is economic recession, a decline in
economic activity for which there is no single formal
definition. However, it is often described in terms of
recession factors such as GDP, the Gini index, or inflation,
all of which are examples of spatial time series data, and
whose change can be a clear indicator of the state of the
economy. As recession analysis is a very complex topic and
it is not entirely clear which economic factors have the
greatest impact, purely automated techniques are not
appropriate and there is scope for advances in analytical
approaches. This thesis proposes an application “Recession
Explorer”: visual analytics of economic recession and its
forecasting as an example of a holistic system that displays
spatial time series data and explores patterns and insights
in the data. Such a combination of approaches provides a
unique perspective on economic recession studies by
facilitating both high-level human reasoning and the use of
advanced mathematical algorithms. The goal of the
application is to demonstrate that the use of visual
analytics is a beneficial approach to address the challenges
of economic recession and, more generally, to assist users
with interactive visualisations when dealing with and
analysing spatial time series data.",
month = oct,
pages = "60",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Research Unit of Computer Graphics, Institute of Visual
Computing and Human-Centered Technology, Faculty of
Informatics, TU Wien",
keywords = "visual analytics, interactive visual analysis, machine
learning, linear regression, elastic net, K-Means,
classification, spatial time series, economic recession,
recession factors",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2021/Priselac2021/",
}
 image
image Master Thesis
Master Thesis Poster
Poster


