Information
- Publication Type: Conference Paper
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: October 2021
- ISBN: 978-3-03868-162-5
- Publisher: Eurographics Association
- Organization: The Eurographics Association
- Location: online
- Lecturer: Stefan Stappen
- Event: Pacific Graphics 2021
- Editor: Lee, Sung-Hee and Zollmann, Stefanie and Okabe, Makoto and Wünsche, Burkhard
- DOI: 10.2312/pg.20211391
- Call for Papers: Call for Paper
- Booktitle: Pacific Graphics Short Papers, Posters, and Work-in-Progress Papers
- Pages: 2
- Conference date: 18. October 2021 – 21. October 2021
- Pages: 65 – 66
- Keywords: variable rate shading, temporal antialiasing
Abstract
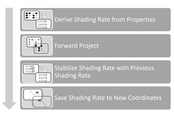
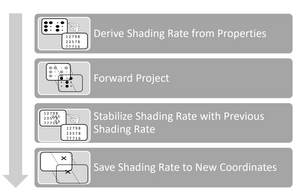
We propose two novel methods to improve the efficiency and quality of real-time rendering applications: Texel differential-based content-adaptive shading (TDCAS) and spatio-temporally filtered adaptive shading (STeFAS). Utilizing Variable Rate Shading (VRS)-a hardware feature introduced with NVIDIA's Turing micro-architecture-and properties derived during rendering or Temporal Anti-Aliasing (TAA), our techniques adapt the resolution to improve the performance and quality of real-time applications. VRS enables different shading resolution for different regions of the screen during a single render pass. In contrast to other techniques, TDCAS and STeFAS have very little overhead for computing the shading rate. STeFAS enables up to 4x higher rendering resolutions for similar frame rates, or a performance increase of 4× at the same resolution.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
- Entry in reposiTUm (TU Wien Publication Database)
- Entry in the publication database of TU-Wien
- DOI: 10.2312/pg.20211391
BibTeX
@inproceedings{stappen_SteFAS,
title = "Temporally Stable Content-Adaptive and Spatio-Temporal
Shading Rate Assignment for Real-Time Applications",
author = "Stefan Stappen and Johannes Unterguggenberger and Bernhard
Kerbl and Michael Wimmer",
year = "2021",
abstract = "We propose two novel methods to improve the efficiency and
quality of real-time rendering applications: Texel
differential-based content-adaptive shading (TDCAS) and
spatio-temporally filtered adaptive shading (STeFAS).
Utilizing Variable Rate Shading (VRS)-a hardware feature
introduced with NVIDIA's Turing micro-architecture-and
properties derived during rendering or Temporal
Anti-Aliasing (TAA), our techniques adapt the resolution to
improve the performance and quality of real-time
applications. VRS enables different shading resolution for
different regions of the screen during a single render pass.
In contrast to other techniques, TDCAS and STeFAS have very
little overhead for computing the shading rate. STeFAS
enables up to 4x higher rendering resolutions for similar
frame rates, or a performance increase of 4× at the same
resolution.",
month = oct,
isbn = "978-3-03868-162-5",
publisher = "Eurographics Association",
organization = "The Eurographics Association",
location = "online",
event = "Pacific Graphics 2021",
editor = "Lee, Sung-Hee and Zollmann, Stefanie and Okabe, Makoto and
W\"{u}nsche, Burkhard",
doi = "10.2312/pg.20211391",
booktitle = "Pacific Graphics Short Papers, Posters, and Work-in-Progress
Papers",
pages = "2",
pages = "65--66",
keywords = "variable rate shading, temporal antialiasing",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2021/stappen_SteFAS/",
}

 paper
paper