Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: June 2022
- Journal: Computer Graphics Forum
- Volume: 41
- Open Access: yes
- Event: Proceedings Eurographics/IEEE Symposium on Visualization, Eurovis 2022
- Call for Papers: Call for Paper
- Conference date: 11. November 2021 – 15. June 2022
Abstract
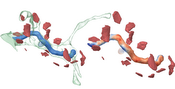
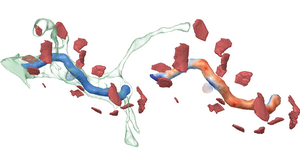
High-resolution electron microscopy imaging allows neuroscientists to reconstruct not just entire cells but individual cell sub-structures (i.e., cell organelles) as well. Based on these data, scientists hope to get a better understanding of brain function and development through detailed analysis of local organelle neighborhoods. In-depth analyses require efficient and scalable comparison of a varying number of cell organelles, ranging from two to hundreds of local spatial neighborhoods. Scientists need to be able to analyze the 3D morphologies of organelles, their spatial distributions and distances, and their spatial correlations. We have designed Barrio as a configurable framework that scientists can adjust to their preferred workflow, visualizations, and supported user interactions for their specific tasks and domain questions. Furthermore, Barrio provides a scalable comparative visualization approach for spatial neighborhoods that automatically adjusts visualizations based on the number of structures to be compared. Barrio supports small multiples of spatial 3D views as well as abstract quantitative views, and arranges them in linked and juxtaposed views. To adapt to new domain-specific analysis scenarios, we allow the definition of individualized visualizations and their parameters for each analysis session. We present an in-depth case study for mitochondria analysis in neuronal tissue and demonstrate the usefulness of Barrio in a qualitative user study with neuroscientists.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@article{Troidl_2022,
title = "Barrio: Customizable Spatial Neighborhood Analysis and
Comparison for Nanoscale Brain Structures",
author = "Troidl Jakob and Corrado Cali and Eduard Gr\"{o}ller and
Hanspeter Pfister and Markus Hadwiger and Johanna Beyer",
year = "2022",
abstract = "High-resolution electron microscopy imaging allows
neuroscientists to reconstruct not just entire cells but
individual cell sub-structures (i.e., cell organelles) as
well. Based on these data, scientists hope to get a better
understanding of brain function and development through
detailed analysis of local organelle neighborhoods. In-depth
analyses require efficient and scalable comparison of a
varying number of cell organelles, ranging from two to
hundreds of local spatial neighborhoods. Scientists need to
be able to analyze the 3D morphologies of organelles, their
spatial distributions and distances, and their spatial
correlations. We have designed Barrio as a configurable
framework that scientists can adjust to their preferred
workflow, visualizations, and supported user interactions
for their specific tasks and domain questions. Furthermore,
Barrio provides a scalable comparative visualization
approach for spatial neighborhoods that automatically
adjusts visualizations based on the number of structures to
be compared. Barrio supports small multiples of spatial 3D
views as well as abstract quantitative views, and arranges
them in linked and juxtaposed views. To adapt to new
domain-specific analysis scenarios, we allow the definition
of individualized visualizations and their parameters for
each analysis session. We present an in-depth case study for
mitochondria analysis in neuronal tissue and demonstrate the
usefulness of Barrio in a qualitative user study with
neuroscientists.",
month = jun,
journal = "Computer Graphics Forum",
volume = "41",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2022/Troidl_2022/",
}

 Image
Image Paper
Paper