Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: January 2024
- Journal: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
- Volume: 30
- Open Access: yes
- Number: 1
- Location: Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
- Lecturer: Lukas Herzberger

- ISSN: 1941-0506
- Event: IEEE VIS 2023
- DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2023.3327193
- Pages: 11
- Publisher: IEEE
- Conference date: 22. October 2023
– 27. October 2023
- Pages: 1380 – 1390
- Keywords: Rendering (computer graphics), Octrees, Spatial resolution, Graphics processing units, Data visualization, Optimization, Standards, Volume rendering, Ray-guided rendering, Large-scale data, Out-of-core rendering, Multi-resolution, Multi-channel, Web-Based Visualization
Abstract
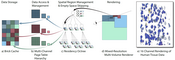
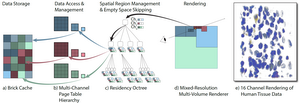
We present a hybrid multi-volume rendering approach based on a novel Residency Octree that combines the advantages of out-of-core volume rendering using page tables with those of standard octrees. Octree approaches work by performing hierarchical tree traversal. However, in octree volume rendering, tree traversal and the selection of data resolution are intrinsically coupled. This makes fine-grained empty-space skipping costly. Page tables, on the other hand, allow access to any cached brick from any resolution. However, they do not offer a clear and efficient strategy for substituting missing high-resolution data with lower-resolution data. We enable flexible mixed-resolution out-of-core multi-volume rendering by decoupling the cache residency of multi-resolution data from a resolution-independent spatial subdivision determined by the tree. Instead of one-to-one node-to-brick correspondences, each residency octree node is mapped to a set of bricks from different resolution levels. This makes it possible to efficiently and adaptively choose and mix resolutions, adapt sampling rates, and compensate for cache misses. At the same time, residency octrees support fine-grained empty-space skipping, independent of the data subdivision used for caching. Finally, to facilitate collaboration and outreach, and to eliminate local data storage, our implementation is a web-based, pure client-side renderer using WebGPU and WebAssembly. Our method is faster than prior approaches and efficient for many data channels with a flexible and adaptive choice of data resolution.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{herzberger-2024-roh,
title = "Residency Octree: a hybrid approach for scalable web-based
multi-volume rendering",
author = "Lukas Herzberger and Markus Hadwiger and Robert Kr\"{u}ger
and Peter K Sorger and Hanspeter Pfister and Eduard
Gr\"{o}ller and Johanna Beyer",
year = "2024",
abstract = "We present a hybrid multi-volume rendering approach based on
a novel Residency Octree that combines the advantages of
out-of-core volume rendering using page tables with those of
standard octrees. Octree approaches work by performing
hierarchical tree traversal. However, in octree volume
rendering, tree traversal and the selection of data
resolution are intrinsically coupled. This makes
fine-grained empty-space skipping costly. Page tables, on
the other hand, allow access to any cached brick from any
resolution. However, they do not offer a clear and efficient
strategy for substituting missing high-resolution data with
lower-resolution data. We enable flexible mixed-resolution
out-of-core multi-volume rendering by decoupling the cache
residency of multi-resolution data from a
resolution-independent spatial subdivision determined by the
tree. Instead of one-to-one node-to-brick correspondences,
each residency octree node is mapped to a set of bricks from
different resolution levels. This makes it possible to
efficiently and adaptively choose and mix resolutions, adapt
sampling rates, and compensate for cache misses. At the same
time, residency octrees support fine-grained empty-space
skipping, independent of the data subdivision used for
caching. Finally, to facilitate collaboration and outreach,
and to eliminate local data storage, our implementation is a
web-based, pure client-side renderer using WebGPU and
WebAssembly. Our method is faster than prior approaches and
efficient for many data channels with a flexible and
adaptive choice of data resolution.",
month = jan,
journal = "IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics",
volume = "30",
number = "1",
issn = "1941-0506",
doi = "10.1109/TVCG.2023.3327193",
pages = "11",
publisher = "IEEE",
pages = "1380--1390",
keywords = "Rendering (computer graphics), Octrees, Spatial resolution,
Graphics processing units, Data visualization, Optimization,
Standards, Volume rendering, Ray-guided rendering,
Large-scale data, Out-of-core rendering, Multi-resolution,
Multi-channel, Web-Based Visualization",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2024/herzberger-2024-roh/",
}

 paper
paper