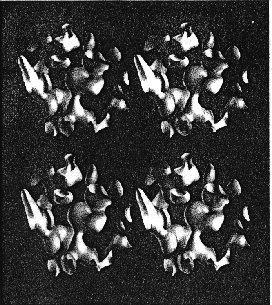Next: Object space coherence
Up: Technics exploiting pixel space
Previous: Raytracing [#BFGS##1#]
An initial image is generated by casting a uniform but sparse grid of rays
into the volume data, interpolating between the resulting colors and
resampling at the display resolution. A sampling rate of one ray per four
pixels corresponding to a sampling rate of one ray per four voxels, is
typical. Subsequent images are generated by discarding interpolated colors,
casting more rays and repeating the interpolation and resampling
steps. Recursive subdivision and based on color differences is used to
concentrate these additional rays in regions of high image complexity and
recursive bi-linear interpolation is used to to form images from the resulting
non-uniform array of colors.
The cost of computing each image in a refinement sequenz is equal to the sum
of the costs of recursive subdivision, ray tracing and recursive
interpolation.
Algorithm:
The voxel array the following algorithm is applied to is already shaded and
classified.
- The image plane is divided into square sample regions measuring
 pixels on a side.
pixels on a side. - Parallel viewing rays are cast into the voxel array from the four corner
pixels of each region.
- Each ray is devided into equal-size sample intervals and color and
opacity is computed at the center of each interval by tri-linear
interpolation of the colors and opacities of the nearest eight voxels.
- The resampled colors and opacities are then composited to yield a color
for the ray.
- If the range of colors returned by the four rays in a sample region is
less than some
 , no further processing is performed on the region,
otherwise the region is divided into four subregions and more rays are cast.
, no further processing is performed on the region,
otherwise the region is divided into four subregions and more rays are cast. - Subdivision is continues until the range of colors falls below
 or the size of the region reaches some
or the size of the region reaches some 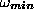 .
. - An image is formed by interpolating between the available colors (to
ensure continuity): The
image plane is devided again into square regions measuring
 . Pixels are interpolated at the midpoints of the four sides
and at the center of each region. The region is then subdivided into four
subregions and the process is repeated. Subdivision continues until the
region contains only one pixel.
. Pixels are interpolated at the midpoints of the four sides
and at the center of each region. The region is then subdivided into four
subregions and the process is repeated. Subdivision continues until the
region contains only one pixel. - To refine the image all interpolated pixels are cleared, the level of
detail is increased by decreasing
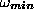 ,
,  and/or
and/or
 and repeating the the algorithm.
To avoid that the same rays are cast several times a flag is maintained for
each pixel.
and repeating the the algorithm.
To avoid that the same rays are cast several times a flag is maintained for
each pixel.
Problems:
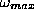
High values of  cause features to missed, high values of
cause features to missed, high values of
 cause features to be ignored even if they are not missed and high
values of
cause features to be ignored even if they are not missed and high
values of 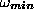 cause features to be poorely resolved even if they
are neither missed or ignored. Inapropriate values for these parameters cause
suboptimal presentation of the data as well as unequal intervalls between
successive frames in refinement sequenzes. Algorithms are needed that
automatically select an optimum sequenz of values based on the characteristics
of a particular dataset.
cause features to be poorely resolved even if they
are neither missed or ignored. Inapropriate values for these parameters cause
suboptimal presentation of the data as well as unequal intervalls between
successive frames in refinement sequenzes. Algorithms are needed that
automatically select an optimum sequenz of values based on the characteristics
of a particular dataset.
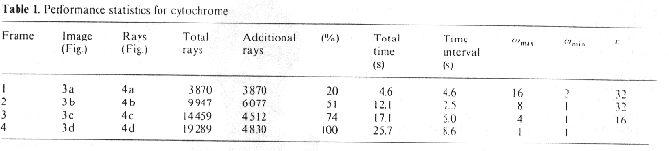
Results:
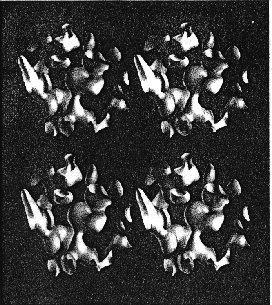





Next: Object space coherence
Up: Technics exploiting pixel space
Previous: Raytracing [#BFGS##1#]
Lukas Mroz
Tue Feb 9 12:46:24 MET 1999
![]() cause features to missed, high values of
cause features to missed, high values of
![]() cause features to be ignored even if they are not missed and high
values of
cause features to be ignored even if they are not missed and high
values of ![]() cause features to be poorely resolved even if they
are neither missed or ignored. Inapropriate values for these parameters cause
suboptimal presentation of the data as well as unequal intervalls between
successive frames in refinement sequenzes. Algorithms are needed that
automatically select an optimum sequenz of values based on the characteristics
of a particular dataset.
cause features to be poorely resolved even if they
are neither missed or ignored. Inapropriate values for these parameters cause
suboptimal presentation of the data as well as unequal intervalls between
successive frames in refinement sequenzes. Algorithms are needed that
automatically select an optimum sequenz of values based on the characteristics
of a particular dataset.