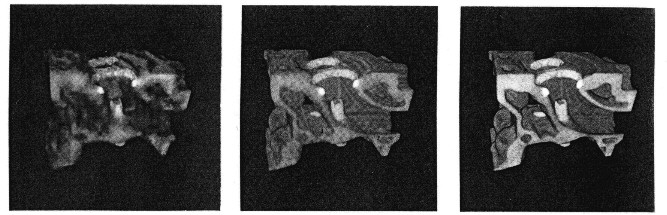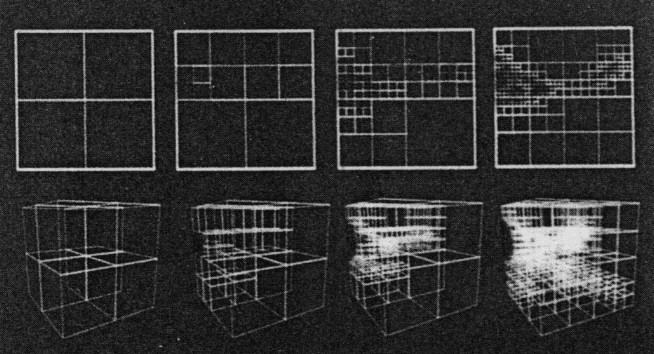
The Hierarchical Splatting ([4]) group as
large as possible homogeneous sections in the volume and consider it as
one large cell. Such a cell is approximated with one large splat, which
is projected on the image plane. Every node of the pyramid contains the
average RGB and alpha of its children and the associated average error
if you approximate this region with one average splat, instead of using
the original volume data. For adjusting progressive refinement you choose
an error which is a measure for the wanted homogeneity. With the user-specified
error you determine the traversal through the pyramid. You move down the
pyramid until the error in a node is less equal than the desired error
or homogeneity. Now the whole volume data is decomposed in cubes of different
sizes depending on their homogeneity.

If you select a large error the volume is decomposed in fewer subvolumes,
the number increases with decreasing error. For every level of the pyramid
are calculated proper sized footprint tables, which are used for projecting
and compositing cells of this level. Further the splats are approximated
with Gouraud shaded RGBA polygons, so you can use hardware for compositing
and drawing.