The current acquisition pipeline for visual models of 3D worlds is based on a paradigm of planning a goal-oriented acquisition - sampling on site - processing. The digital model of an artifact (an object, a building,up to an entire city) is produced by planning a specific scanning campaign, carefully selecting the (often costly) acquisition devices, performing the on-site acquisition at the required resolution and then post-processing the acquired data to produce a beautified triangulated and textured model. However, in the future we will be faced with the ubiquitous availability of sensing devices that deliver different data streams that need to be processed and displayed in a new way, for example smartphones, commodity stereo cameras, cheap aerial data acquisition devices, etc. We therefore propose a radical paradigm change in acquisition and processing technology: instead of a goal-driven acquisition that determines the devices and sensors, we let the sensors and resulting available data determine the acquisition process. Data acquisition might become incidental to other tasks that evices/people to which sensors are attached carry out. A variety of challenging problems need to be solved to exploit this huge amount of data, including: dealing with continuous streams of time-dependent data, finding means of integrating data from different sensors and modalities, detecting changes in data sets to create 4D models, harvesting data to go beyond simple 3D geometry, and researching new paradigms for interactive inspection capabilities with 4D data sets. In this project, we envision solutions to these challenges, paving the way for affordable and innovative uses of information technology in an evolving world sampled by ubiquitous visual sensors. Our approach is high-risk and an enabling factor for future visual applications. The focus is clearly on basic research questions to lay the foundation for the new paradigm of incidental 4D data capture.
Funding
- EU 7th Framework Program 323567
Team
News
Research Areas
- In this area, we concentrate on algorithms that synthesize images to depict 3D models or scenes, often by simulating or approximating the physics of light.
- Uses concepts from applied mathematics and computer science to design efficient algorithms for the reconstruction, analysis, manipulation, simulation and transmission of complex 3D models. Example applications are collision detection, reconstruction, compression, occlusion-aware surface handling and improved sampling conditions.
- In this area, we focus on researching methods and algorithms that facilitate creation, representation, analysis and processing of 3D models.
Publications
| Image | Bib Reference | Publication Type |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | ||
 |
Florian Laager Robust Registration of Range Images [  image] [ image] [ thesis] thesis] |
Master Thesis |
| 2016 | ||
 |
Maximilian Mayrhauser Migration of Surface Curve to Most Concave Isoline |
Bachelor Thesis |
 |
Tamy Boubekeur, Paolo Cignoni, Elmar Eisemann, Michael Goesele, Reinhard Klein, Stefan Roth, Michael Weinmann, Michael Wimmer Harvesting Dynamic 3DWorlds from Commodity Sensor Clouds In Proceedings of the 14th Eurographics Workshop on Graphics and Cultural Heritage, pages 19-22. October 2016. |
Conference Paper |
 |
Markus Schütz Potree: Rendering Large Point Clouds in Web Browsers [  thesis] thesis] |
Master Thesis |
 |
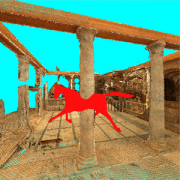
Murat Arikan, Reinhold Preiner , Michael Wimmer , Michael Wimmer Multi-Depth-Map Raytracing for Efficient Large-Scene Reconstruction IEEE Transactions on Visualization & Computer Graphics, 22(2):1127-1137, February 2016. [  draft] [ draft] [ image] image] |
Journal Paper (without talk) |
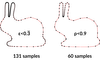 |
Stefan Ohrhallinger , Scott A. Mitchell, Michael Wimmer , Scott A. Mitchell, Michael Wimmer Curve Reconstruction with Many Fewer Samples Computer Graphics Forum, 35(5):167-176, 2016. [  paper] [ paper] [ slides] [Reproducibility Source Code] slides] [Reproducibility Source Code] |
Journal Paper with Conference Talk |
| 2015 | ||
 |
Markus Schütz , Michael Wimmer , Michael Wimmer High-Quality Point Based Rendering Using Fast Single Pass Interpolation In Proceedings of Digital Heritage 2015 Short Papers, pages 369-372. September 2015. [  draft] draft] |
Conference Paper |
| 2014 | ||
 |
Murat Arikan, Reinhold Preiner , Claus Scheiblauer, Stefan Jeschke, Michael Wimmer , Claus Scheiblauer, Stefan Jeschke, Michael Wimmer Large-Scale Point-Cloud Visualization through Localized Textured Surface Reconstruction IEEE Transactions on Visualization & Computer Graphics, 20(9):1280-1292, September 2014. [  draft] [ draft] [ image] image] |
Journal Paper (without talk) |
 |
Reinhold Preiner , Oliver Mattausch , Oliver Mattausch , Murat Arikan, Renato Pajarola, Michael Wimmer , Murat Arikan, Renato Pajarola, Michael Wimmer Continuous Projection for Fast L1 Reconstruction ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH 2014), 33(4):47:1-47:13, August 2014. [  paper_small] [ paper_small] [ paper] [ paper] [ video] video] |
Journal Paper with Conference Talk |
 |
Mohamed Radwan, Stefan Ohrhallinger , Michael Wimmer , Michael Wimmer Efficient Collision Detection While Rendering Dynamic Point Clouds In Proceedings of the 2014 Graphics Interface Conference, pages 25-33. May 2014. [  paper] [ paper] [ slides] slides] |
Conference Paper |
 |
Claus Scheiblauer Interactions with Gigantic Point Clouds Supervisor: Michael Wimmer  Duration: December 2006 — July 2014 [  thesis] thesis] |
PhD-Thesis |
Michael Wimmer Do we need the full reconstruction pipeline?, 24. July 2014, Vienna, Austria |
Invited Talk | |