The view frustum :
- Size of the view frustum
 volume.
volume. - View frustum position and orientation is defined by
position p and with an orientation
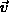 .
. - Depth of view is fixed d.
- An arbitrary path is traced through the volume and is defined
by a discrete sequence of viewing sites
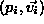 where
where 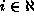 whose values are not known in
advance.
whose values are not known in
advance. - The path is sequence of incremental steps in a direction or rotations about an axis.
The coherence between nearby frames f is used.
The results from the computation of a given view are used to
compute f successive frames, after which a refresh view must
be produced.
Sampling is obtaining the color and opacity of a point in
the ray. (Interpolation, Transfer functions mapping, and
shading or light calculation).
Composition is Volumetric composition equation in a
front to back.
The algorithm is divided in 2 phases.
 ):
Short ray segments are cast composite color computing the
composite color and transparency for each segment.
):
Short ray segments are cast composite color computing the
composite color and transparency for each segment. Assumed that the sampling rate is
- The sample points are divided into L levels where
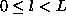 based on the distance from the viewpoint.
based on the distance from the viewpoint. -
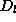 distance of the first sample of level l.
distance of the first sample of level l. - Each level l consist of a set of ray segments
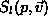 or
or 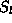 that treat the samples from
that treat the samples from 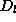 to
to
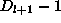 (
( 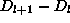 samples).
samples). -
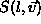 or
or 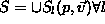
- Result phase 1 L two-dimensional arrays.
- Each level can be sampled at different
resolutions.
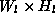 horizontal and vertical resolutions of
the segments casts in level l.
horizontal and vertical resolutions of
the segments casts in level l.
With that they can get adaptive sampling to avoid undersampling of distance points. Trying to maintain similar lateral sampling.
Avoid oversampling in the regions near the viewpoint. The few levels near the view point cast very few rays /it Acceleration.
Figure: 2D illustration of the segments computed by the
two-phase algorithm. The horizontal lines represent the
rectangles into which the segments are to be mapped
-
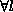 do from
do from 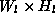 to Screen
resolution.
to Screen
resolution. - alpha blending
- Define a rectangle for any level
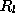
- Drawn
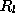 with
with 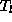 mapped at distance
mapped at distance
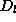 perpendicular two the view direction and
from front to back and Alpha blending.
perpendicular two the view direction and
from front to back and Alpha blending. - Special treatment of
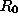 Drawn between 0 and
Drawn between 0 and
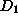 .
.
- Brute force raycasting is an special case of two-phase
algorithm in which
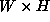 are cast to Depth d in a single
level.
are cast to Depth d in a single
level. - 10 Levels and 0.385 times as many sample steps as the
brute force approach. See table 1 in figure
 .
. - Composing operation is nonlinear reordering
interpolation and the composite steps will incur some
error. See figure
 to do a visual comparison
between brute force and two phase ray casting.
to do a visual comparison
between brute force and two phase ray casting.
Figure: Rendering comparison:
a) Brute force perspective raycasting.
b) The two phase algorithm.
c) Difference between the two multiplied by 10.
Figure: Tables of times and comparisons
-
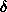 radius from the base position.
radius from the base position. -
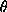 angle of the original viewing
direction.
angle of the original viewing
direction. -
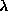 levels that need to be recalculated in
every step. So reused
levels that need to be recalculated in
every step. So reused 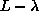 .
.
 ).given
).given -
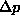 is the position increment
is the position increment
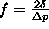 .
. -
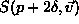 next predicted
structure. Computing
next predicted
structure. Computing 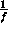 of it in any step.
of it in any step. - The first
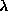 levels move with viewpoint.
levels move with viewpoint. - The depth of levels
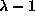 varies by the amount
varies by the amount
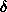 .
.
- For each step one plane of samples should be rendered onto the back of the last level so that the total viewing depth remain the same.
- Calculate an slightly larger field of view for the
positions behind
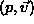 the frustum.
the frustum. - Fixed
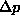 . Higher f less quality.
. Higher f less quality.
Figure: 2D illustration of the resampling of S during translation
PROBLEM It implies bigger
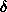 and this
implies the orientation of the S on the periphery of the
view do not match.( See figure
and this
implies the orientation of the S on the periphery of the
view do not match.( See figure  )
)
The new segment s is bilaterally interpolated by the 4 segments nearest to s which is not parallel to the 4. Which are the weights distance of the interpolation?
SOLUTIONS Average Distance or the resampling depends upon relative distance within the plane of the rectangle. Towards the edges the weighting is closer to the middle of the segments. In the middle distances are based on the position of the front.
 )given
)given
Figure: The initial segment data structure is depicted in
gray and should be 2 ![]() wider that the field of view
wider that the field of view
-
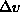 incremental in angle rotation in a
axes.
incremental in angle rotation in a
axes. - the size of the viewing frustum in the
direction of rotation is
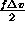 wider.
wider. -
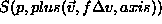 is the next
predicted structure.
is the next
predicted structure. - levels from 0 to
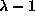 don't need to be
recomputed at each step.
don't need to be
recomputed at each step. - More resampling accuracy than translation. No error in the orientation of the segments. Relative distance are well defined.
 )
in order to compare time savings.
)
in order to compare time savings.
Figure: Tables of times and comparisons